Digital signature is a security mechanism system in the cyberspace for digital data transformation by attaching a code on the document records. It is used to encrypt message before transformations and to decrypt them on receiving time.
- It requires a key pair (private key for encryption and public key for decryption), which are used to encrypt and decrypt the messages. Digital signatures are especially important for electronic commerce and a key component of most authentication schemes. It stops the unauthorized access of digital transaction.
- Digital signature law provides a legal framework to facilitate and safeguard electronic transaction in the electronic medium.
- What is Private key?
- It is the key that is allocated to a particular person for his private purpose. This key is kept secret and is known to him only.
- What is Public key?
- A public key is a collected to a person to distribute to other particles. A message that is locked by a private key can only be unlocked by the corresponding public key and vice versa.
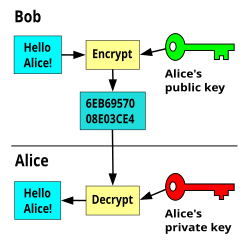
- For example
- If Bob wants to send sensitive data to Alice, and wants to be sure that only Alice may be able to read it, he will encrypt the data with Alice's Public Key. Only Alice has access to her corresponding Private Key and as a result is the only person with the capability of decrypting the encrypted data back into its original form.
As only Alice has access to her Private Key, it is possible that only Alice can decrypt the encrypted data. Even if someone else gains access to the encrypted data, it will remain confidential as they should not have access to Alice's Private Key.